Table of Contents Link to heading
- Virtualisation Concepts
- Managing Resources
- High Availability and Disaster Recovery
- Migration
- Other VMware Datacenter Software
Virtualisation Concepts Link to heading
Virtual Resources Link to heading
Processor (CPU) Link to heading
Memory (RAM) Link to heading
Due to how RAM is virtualised, the hypervisor is able to allocate more RAM to VMs than exists in the physical host. This is done by creating a swap file on disk that is used as RAM in the case that not enough physical RAM is available. This is called over-commitment of resources
Hard Disk Link to heading
In a virtualized environment, the “hard disk” is a set of files that exist on a physical storage device—rather than an actual physical device
VMDKs are commonly stored on a storage area network (SAN) to enable accessibility from multiple hosts.
Network Link to heading
Virtual Machines Link to heading
VMs are a core building block of the Software Defined Datacenter (SDDC) that enables you to take existing physical servers and repurpose and consolidate them.
Hypervisors Link to heading
There are two basic types of hypervisors:
- Bare-metal hypervisors: Acts like a lightweight OS, running directly on
physical hardware.
- E.g., VMware ESXi and Microsoft Hyper-V.
- Isolated from the attack-prone OS, it’s highly secure.
- Hosted hypervisors: Runs as a software layer on an existing OS, similar
to other computer programs.
- E.g., VMware Workstation/Fusion and Parallels Desktop.
- The added level of a host OS that significantly reduces the performance of the VMs because the hypervisor doesn’t have ultimate control of the resources.
Managing Resources Link to heading
vCenter Server Link to heading
The component of the vSphere suite that ties all of the other components together, providing a centralised platform for managing vSphere environments, automating many complex tasks.
- Automation: Unlocks the power of vSphere through proactive management
- Scalability: Scalable and extensible management platform
- Visibility: Deep visibility into entry level of the virtual infrastructure
After a host is added to the vCenter Server inventory, vCenter provides the following functions:
- Simple deployment: Templates, host profiles, cloning VMs, and vApps.
- Centralised control and visibility: vSphere Web Client to manage the environment from any browser, vCenter Single Sign-On for authentication, customised roles and permissions, and inventory searching.
- Proactive optimisation and availability: Resource management, Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS), Distributed Power Management (DPM), VMware high availability (HA), and vSphere App HA.
- Management: vCenter Orchestrator to automate management tasks, performance data, task and event logs, and API access.
Clusters Link to heading
When adding a host to vCenter server, you must add it somewhere in the hierarchy. The hierarchy in most cases will have at least one datacenter that contains either individually managed hosts or clusters of hosts.
Managed Hosts Link to heading
Clusters of Hosts Link to heading
High Availability and Disaster Recovery Link to heading
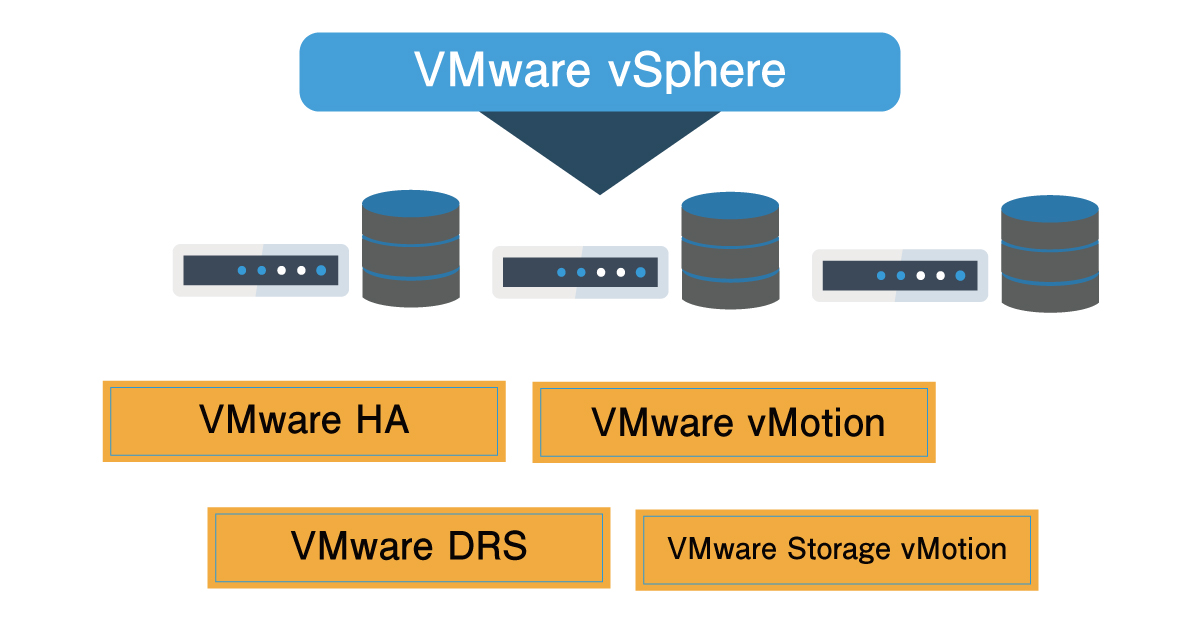
VMware provides high availability (HA) and disaster recovery (DR) solutions to ensure business continuity in case of failures or outages. These solutions include:
- VMware vSphere High Availability (HA): Automatically restarts virtual machines (VMs) on available hosts when a failure occurs.
- VMware vMotion: Enables live migration of VMs between hosts without downtime.
- VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM): Automates disaster recovery workflows, ensuring fast failover and failback.
- VMware HCX Disaster Recovery: Provides active-active protection for VMs across private and public clouds, allowing scheduled backups and large-scale workload migration.
Migration Link to heading
VMware offers multiple migration options to move workloads efficiently:
- vMotion: Live migration of running VMs between hosts.
- Storage vMotion: Moves VM disk files between storage locations without downtime.
- VMware HCX: Simplifies large-scale application migration across on-premises and cloud environments.
- VMware vSphere Replication: Enables asynchronous replication of VMs across different sites for disaster recovery and migration.
Other VMware Datacenter Software Link to heading
VMware provides additional software solutions for datacenter management:
- VMware NSX: A network virtualization platform for secure and scalable networking.
- VMware vSAN: A software-defined storage solution that integrates with vSphere.
- VMware Cloud Foundation: A hybrid cloud platform combining compute, storage, networking, and management.
- VMware Tanzu: A Kubernetes-based solution for modern application development.
These tools enhance virtualization, security, and scalability across enterprise datacenters.