Table of Contents Link to heading
- What is a Function
- Working with String
SUBSTRINGfunctionCHARINDEXfunction- Example of working with string
- Working with date
CASTfunctionISNULLfunction
What is a Function Link to heading
Functions are calculations performed by the Database Management System (DBMS).
Working with String Link to heading
Common functions include:
| Function | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|
| UPPER(col) | UPPER(‘Sam’) | Sam -> SAM |
| LOWER(col) | LOWER(‘Sam’) | Sam -> sam |
| RTRIM(col) | RTRIM(‘Sam ‘) | [ Sam M ] -> [ Sam M] |
| LTRIM(col) | LTRIM(’ Sam’) | [ M Sam ] -> [M Sam ] |
| LEN(col) | LEN(‘Sam’) | 3 |
| REVERSE(col) | REVERSE(‘Sam’) | Sam -> maS |
| LEFT(string, length) | LEFT(‘Sam’, 2) | Sam -> Sa |
| RIGHT(string, length) | RIGHT(‘Sam’, 2) | Sam -> am |
Example: Link to heading
SELECT UPPER ('Eynesbury') AS [School Name]
Result:
| School Name |
|---|
| EYNESBURY |
SUBSTRING function
Link to heading
Syntax Link to heading
SUBSTRING ( expression, start, length )
- Returns part of a character or text in SQL server.
Arguments Link to heading
- expression
- A character or text.
- start
- An integer that specifies where the returned characters start.
- If start is less than 1, the returned expression will begin at the first character specified in expression.
- If start is greater than the number of characters in the value expression, a zero-length expression is returned.
- length
- A positive integer that specifies how many characters of the expression will be returned.
- If the sum of start and length is greater than the number of characters in expression, the whole value expression beginning at start is returned.
- If length is negative, an error is raised and the statement is terminated.
Example: Link to heading
SELECT SUBSTRING ('Eynesbury', 1, 2) AS [School Name];
Result:
| School Name |
|---|
| Ey |
CHARINDEX function
Link to heading
Syntax Link to heading
CHARINDEX ( expressionToFind, expressionToSearch [ , start_location ] )
- Searches an expression for another expression and returns its starting position if found.
Arguments Link to heading
- expressionToFind
- A character expression that contains the sequence to be found.
- expressionToFind is limited to 8000 characters.
- expressionToSearch
- A character expression to be searched.
- start_location
- An integer at which the search starts.
- If start_location is not specified, is a negative number, or is 0, the search starts at the beginning of expressionToSearch.
Example Link to heading
SELECT CHARINDEX ('Fun', 'DatabaseFundamentals') AS counting;
Result:
| counting |
|---|
| 9 |
Example of working with string Link to heading
DECLARE @address varchar(100) = '13 Wayville road, Woodville, SA 5000'
SELECT
LEFT(@address, CHARINDEX(',', @address) - 1) AS streetAddress,
LEFT(secondPart, LEN(secondPart) - CHARINDEX(' ', REVERSE(secondPart)) -1) AS suburb,
RIGHT(secondPart, CHARINDEX(' ', REVERSE(secondPart))) AS state,
REVERSE(SUBSTRING(REVERSE(@address), 1, 4)) AS postcode
FROM (
SELECT
RTRIM(
REVERSE(
SUBSTRING(
REVERSE(@address), 6, LEN(@address) - CHARINDEX(',', @address) – 5
)
)
) AS secondPart
) AS t1;
Result:
| streetAddress | suburb | state | postcode |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13 Wayville road | Woodville | SA | 5000 |
Working with date Link to heading
Below is a list of common functions related to dates:
Today is Monday, 28 March, 2022.
| Function | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|
| GETDATE() | 2022-03-28 | |
| DATEPART(datePart,inputDate) | DATEPART(d, GETDATE()) | 28 |
| DATENAME(datePart,inputDate) | DATENAME(dw, GETDATE()) | Monday |
| DATENAME(m, GETDATE()) | March | |
| DATEADD(datePart, number, date) | DATEADD(d, 6, GETDATE()) | 2022-04-03 |
Arguments Link to heading
- inputDate
- A literal date or an expression that can resolve to a TIME, DATE, SMALLDATETIME, DATETIME, DATETIME2, or DATETIMEOFFSET value.
- datePart
- A part of the date that you want to return.
- The table below lists all valid date part values.
- Note: either upper-case or lower-case letters are acceptable.
| datePart | abbreviation |
|---|---|
| year | yy, yyyy |
| quarter | qq, q |
| month | mm, m |
| dayofyear | dy, y |
| day | dd, d |
| week | wk, ww |
| weekday | dw |
| hour | hh |
| minute | mi, n |
| second | ss, s |
| millisecond | ms |
| microsecond | mcs |
| nanosecond | ns |
| TZoffset | tz |
| ISO_WEEK | isowk, isoww |
DATEPART() vs. DATENAME()
Link to heading
DATENAME() is similar to the DATEPART(), except for the return type.
- DATENAME() returns the date part as a character string.
- DATEPART() returns the date part as an integer.
Example Link to heading
SELECT
DATEPART(year, '2022-03-28') + '1' [datePart],
DATENAME(year, '2022-03-28') + '1' [dateName] ;
Result:
| datePart | dateName |
|---|---|
| 2023 | 20221 |
:link: SQL Server Tutorial
CAST function
Link to heading
Syntax Link to heading
CAST ( expression AS datatype [ ( length ) ] )
- Converts an expression (of any type) into a specified data type.
Arguments Link to heading
- expression
- Any valid expression.
- datatype
- The target data type, such as int, varchar, bit, etc.
- length
- An optional integer that specifies the length of the target data type.
- The default value is 30.
Examples Link to heading
:memo: Change a value to text.
SELECT
CAST (COUNT (A.actorID) AS varchar (50)) AS example1
FROM Actor as A;
:memo: Change a number to text.
SELECT CAST (5 AS varchar(50)) AS example2
:memo: Add dollar sign before money values.
SELECT
'$' + CAST (MAX (E.salary) AS varchar(40)) AS example3
FROM Employee AS E;
ISNULL function
Link to heading
Syntax Link to heading
ISNULL (expression_or_attribute, replacement_value)
- Returns a specified value if the expression is NULL.
- If the expression is NOT NULL, then returns the expression.
Examples Link to heading
SELECT ISNULL ('Hello', 'tandukemai.com') AS example1;
Result
| example1 |
|---|
| Hello |
SELECT ISNULL (NULL, 'tandukemai.com') AS example2;
Result
| example2 |
|---|
| tandukemai.com |
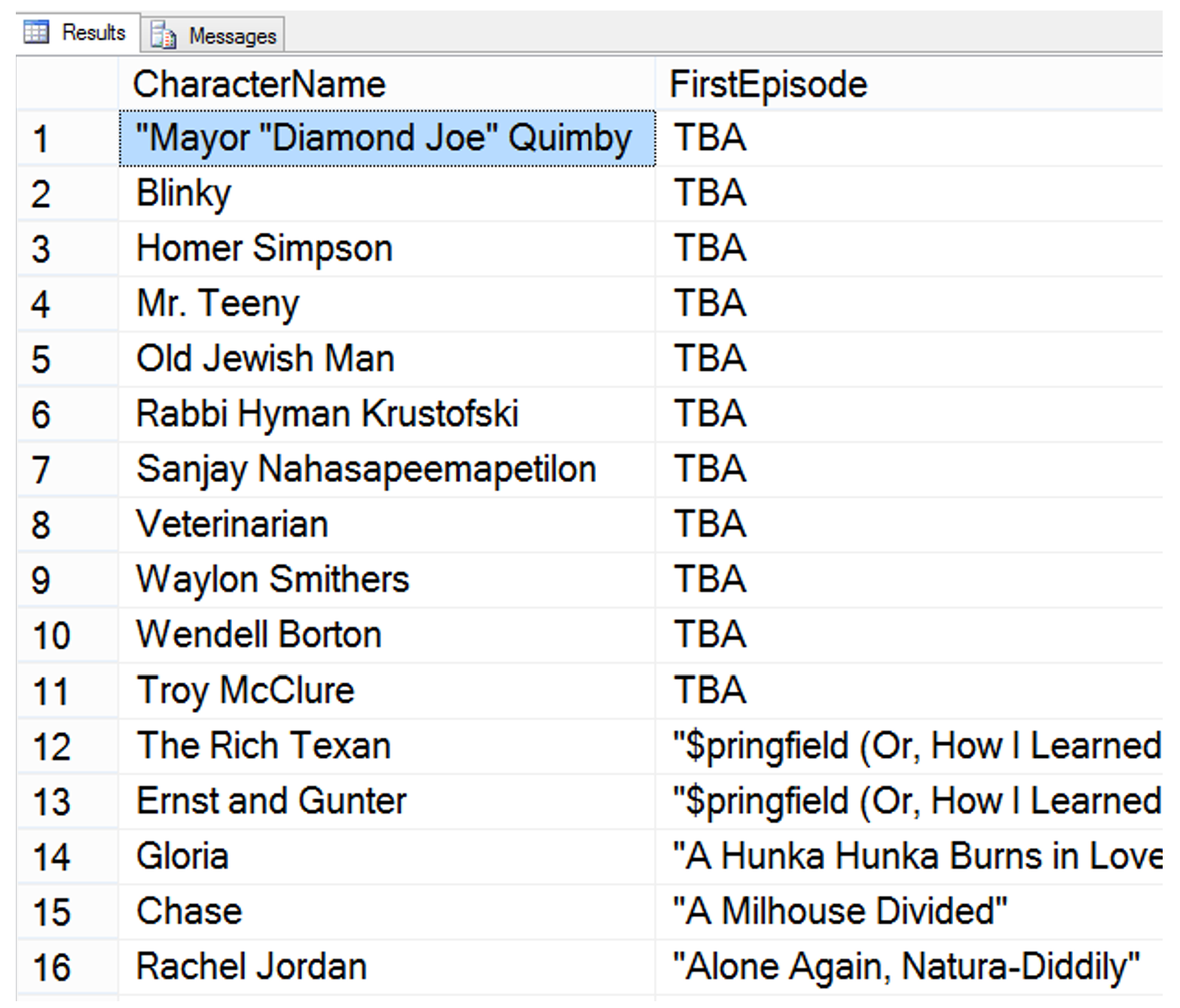
:memo: Find ALL Simpsons characters and their first aired episode; otherwise, display ‘TBA’.
SELECT
CharacterName,
ISNULL (EpisodeName, 'TBA') AS FirstEpisode
FROM Character AS C LEFT OUTER JOIN Episode AS E
ON C.EpisodeID = E.EpisodeID
Sample result: